Proprietary Ratio Definition, Explanation, Formula, Example

It’s an excellent tool for comparing different companies within the same industry, viewing their financial structures, and evaluating their capability to survive in adverse economic scenarios. If the ratio is high, it usually indicates that the company is more solvent, has a lower risk level, and is hence, more attractive to investors or creditors. The ideal ratio of what is the formula for calculating earnings per share eps depends on the nature of the business as well as the investor’s risk appetite.
- Using the proprietary ratio, you can measure the stability of a company’s capital structure.
- When financial leverage increases, the proprietary ratio decreases, signaling that the company is relying more on borrowed funds.
- This means that 70% of TechCo Inc.’s total assets are financed by the shareholders’ equity.
- Proprietary Ratio shows to what degree a company is financed by shareholders, while Debt Ratio shows the proportion of a company’s assets that are financed by creditors.
- Shareholders’ funds include equity, preference share capital, profits or losses, reserves, and surplus.
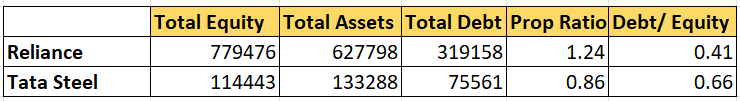
Proprietary Ratio (or Equity Ratio)
It is also be used to compare a company’s financial structure over time or with other companies in the same industry. A Proprietary Ratio, also known as an equity ratio, is a financial metric used by investors and analysts to understand the financial leverage of a company. It compares the shareholder’s equity to the total assets of the company, essentially showing the proportion of a company’s assets financed by stockholders and not creditors. The proprietary ratio is a measure of a company’s financial leverage, which indicates the extent to which it is shareholders’ equity to finance its operations. In other words, it shows what proportion of the total assets is owned by the shareholders.
How does Proprietary Ratio differ from Debt Ratio?
This ratio can be monitored on a trend line or compared with the same metric for competitors to gain a better understanding of the outcome. A high proprietary ratio indicates that a large part of the assets are financed by owners and contributes to the company’s sustainability. On the contrary, a lower ratio may signify higher financial risk as it indicates greater reliance on external liabilities.
How To Calculate The Proprietary Ratio
This means that 70% of TechCo Inc.’s total assets are financed by the shareholders’ equity. This suggests that TechCo Inc. relies less on debt and more on equity for its financing, which could indicate a stronger financial position. However, one would need to compare this ratio with other companies in the same industry to have a better understanding of TechCo Inc.’s relative financial health and risk. The proprietary ratio indicates the proportion of total assets financed by equity rather than debt. When financial leverage increases, the proprietary ratio decreases, signaling that the company is relying more on borrowed funds. High leverage may expose a company to financial risks, which creditors need to monitor closely.
All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. This ratio can be compared to competitors in the same industry, similar companies, or even look at trends over time. Analysts should be monitored on a trend line to gain a reasonable understanding of the ratio.
How PhonePe Earns Money? (PhonePe Business Model Revealed)
A high ratio indicates that the company’s capital structure is strengthening, and the business is increasing its shareholders’ capital while decreasing its debt obligations. This also helps the firm to secure the credibility of the creditors, financiers, and investors. Additionally, the risk of insolvency or bankruptcy reduces considerably, which means the availability of loans at a lower interest rate. However, if the proprietary ratio is too high, the management cannot utilize the debt financing options wisely to generate profit. It is a useful financial measure for evaluating a company’s financial stability and risk profile. The ratio is relevant for investors and creditors interested in understanding how much a company relies on equity rather than debt financing.
A low proprietary ratio shows that a larger portion of the company’s total assets is funded by debt thereby increasing the company’s default risk (which is not favorable for investors and creditors). The Proprietary Ratio, also known as the equity ratio, is a financial metric that indicates the proportion of a company’s total assets that are financed or owned by the owners or shareholders. It is calculated by dividing the total shareholders’ equity by the total assets of the company.
Make sure to include all equity components (equity capital, reserves) and all types of assets (fixed assets, current assets). It is calculated by dividing total assets (i.e., current assets and long-term assets) by tangible network. The proprietary ratio is an important financial ratio as it allows investors and company stakeholders to assess the company’s financial stability. A low proprietary ratio, usually below 50%, suggests that the company is heavily reliant on debt financing. This could raise concerns about the company’s ability to meet its long-term obligations, especially during economic downturns. Creditors and investors may view such a company as riskier, which could lead to higher borrowing costs or difficulty securing financing.
