Small Business Calculators: Quick ratio or acid test ratio
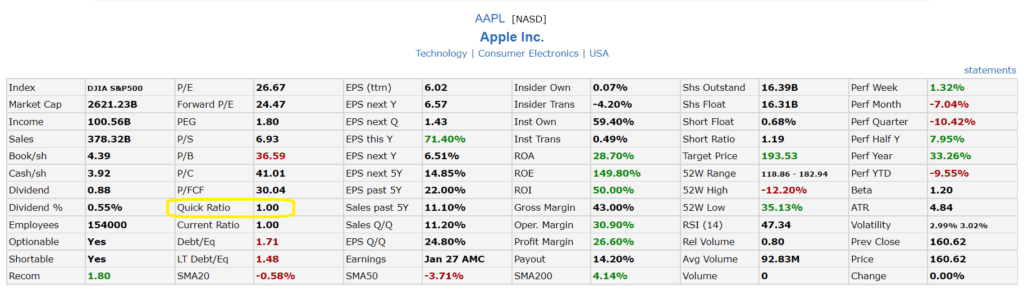
For example, a company may be sitting on a very large cash balance. This capital could be used to generate company growth or invest in new markets. There is often a fine line between balancing short-term cash needs and spending convert from pc to mac capital for long-term potential. Below is the calculation of the quick ratio based on the figures that appear on the balance sheets of two leading competitors operating in the personal care industrial sector, ABC and XYZ.
Pay your team
- If liabilities exceed liquid assets, the ratio will be less than 1, but not negative.
- These are subtracted from current assets to arrive at quick assets, which are divided by current liabilities to get the acid-test ratio.
- Early liquidation or premature withdrawal of assets like interest-bearing securities may lead to penalties or discounted book value.
- There are also considerations to make regarding the true liquidity of accounts receivable as well as marketable securities in some situations.
- The quick ratio can be used to analyze a single company over a period of time or can be used to compare similar companies.
For more information on how Sage uses and looks after your personal data and the data protection rights you have, please read our Privacy Policy. A financial professional will be in touch to help you shortly. This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible.
How to calculate the quick ratio: A step-by-step guide
However, some industries have a much higher quick ratio requirement such as the technology sector which can be as high as 10 or 12. Quick Ratio is also known as the acid-test ratio or liquidity ratio. Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others. Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
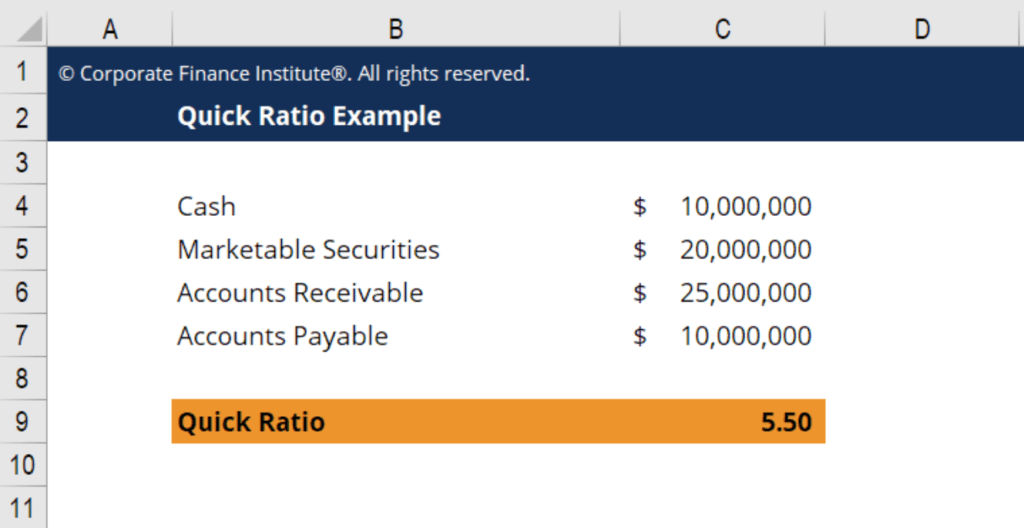
It is calculated by dividing current assets that can be converted into cash in one year, by all current liabilities. Sometimes company financial statements don’t give a breakdown of quick assets on the balance sheet. In this case, you can still calculate the quick ratio even if some of the quick asset totals are unknown. Simply subtract inventory and any current prepaid assets from the current asset total for the numerator.
Date and Time Calculators
Both of these indicators are liquidity ratios used to measure a company’s ability to meet its obligations. However, in the quick ratio, the definition of liquid assets is slightly more restricted as it does not include inventory. But how do you go about finding the current asset, current liability, and inventory numbers you need to calculate the quick ratio? As it turns out, all the data you need is contained within a company’s balance sheet. The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial status at a specific point in time, listing its assets, liabilities, and equity.
Why is it important for a company to have a high quick ratio?
This suggests that the company could theoretically pay off all its short-term liabilities and still have an equal amount of its most liquid assets left over. The Quick Ratio provides a snapshot of a company’s financial health. It indicates if a business can meet its current obligations without experiencing financial strain. For investors, this is invaluable information when considering a potential investment. The quick ratio is calculated by adding cash, cash equivalents, short-term investments, and current receivables together then dividing them by current liabilities. Though other liquidity ratios measure a company’s ability to be solvent in the short term, the quick ratio is among the most aggressive in deciding short-term liquidity capabilities.
But the quick ratio may not capture the profitability or efficiency of the company. The quick ratio does not take into account the collectability of accounts receivables. It also ignores other sources of liquidity, such as credit lines. The quick ratio should not be used by companies that have significant amounts of fixed assets, such as real estate or equipment. It also does not provide information regarding the value of its inventory and marketable securities. While the quick ratio is not a perfect indicator of liquidity, it is one tool that analysts use to get a snapshot of how well a company can meet its short-term obligations.
Examples of marketable securities include stocks and money market funds. But because it does not take into account how long the accounts receivable will be realized as cash, it may still affect the liquidity of the company in a negative way. For example, a company can have a huge amount of accounts receivable that will eventually cause a higher quick ratio. The quick ratio is a simple calculation that can be easily determined using the financial statements of a firm. However, it’s crucial to remember that while a quick ratio of 2 is usually a good sign, it’s not universally so.
The quick ratio is an indicator of a company’s short-term liquidity position and measures a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations with its most liquid assets. The quick ratio and current ratio are accounting formulas small business owners can use to understand liquidity. While the quick ratio uses quick assets, the current ratio uses current assets. The current ratio formula is current assets divided by current liabilities. Another commonly used liquidity ratio is the current ratio, calculated as Current Assets divided by Current Liabilities.
